
THCA vs THCV are two of the most well-known cannabinoids on the market, each related to THC but having distinct chemical structures. Can become psychoactive upon heating through smoking or vaping (decarboxylation), while THCV remains nonpsychoactive until heated by smoking or vaping (decarboxylation).
The world of cannabis is complex and diverse, with hundreds of different cannabinoids present. Two of the most intriguing and lesser-known cannabinoids are THCA and THCV. In this article, we will explore the differences between THCA and THCV, their potential benefits, and how they interact with the body. By understanding these unique cannabinoids, we can better appreciate the potential of the cannabis plant for both recreational and medicinal use.

THCV is an extremely potent cannabinoid with potential applications in treating depression, appetite and pain management as well as offering neuroprotective properties.
Cannabinoids Compared
THCV can be found in cannabis plants, yet does not produce the psychoactive effects typically associate with THC. Instead, it produces an increase in appetite and surge of energy; additionally, it has anti-inflammatory properties and may help lower anxiety; may ease chemotherapy-induced nausea/vomiting as well as digestive disorders like IBS/Crohn’s disease; has neuroprotective qualities as stated by one study published by Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin;

There are three main types of cannabinoids:
- Endocannabinoids (produced naturally by the body)
- Phytocannabinoids (found in cannabis plants)
- Synthetic cannabinoids (created in laboratories)
The most well-known phytocannabinoids are THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol). But there are many others, including THCA and THCV, which have unique properties and potential health benefits.
When heated however, THCa undergoes decarboxylation and turns into THC; though its effects are much milder. THCV can also produce psychoactive effects. However, unlike THC, THCV acts as a CB1 antagonist – blocking receptor activation by CB1. Studies have demonstrated its anti-anxiety properties, as well as being capable of decreasing dopamine and serotonin activity within the brain.
Chemical Structure Differences
THCA and THCV share a typical three-ring structure characteristic of cannabinoids, but they differ in their side chains. This difference in molecular structure is responsible for their unique properties. THCA, for instance, carries a carboxylic acid group in its structure that THCV lacks, contributing to THCA non-psychoactive nature. On the other hand, THCV has a propyl (3-carbon) side chain, as opposed to the pentyl (5-carbon) side chain found in THCA and THCV.
What is THCA?

While decarboxylation sounds like a big word, it’s essentially a scientific way to say “heating the molecule until it changes its molecular shape.” This can be done by cooking, baking, smoking, or vaping.
The removal of this carboxyl group transforms the cannabinoid acid into its corresponding neutral cannabinoid. For example, THCA converts to THC, CBDA (cannabidiolic acid) converts to CBD, CBGA
Cannabinoid acids are typically abundant in raw or unheated cannabis plants. Up until recently, there hasn’t been much research on cannabinoid acids because they were thought of as “unactivated cannabinoids.”
What is THCV?
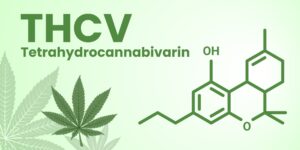
Tetrahydrocannabinovarin (THCV), another cannabinoid found in cannabis plants, can also produce psychoactive effects that can induce high when taken in high doses. Unlike THC however, THCV doesn’t directly interact with CB1 and CB2 receptors to produce its effects; rather its chemical structure allows for weak interactions and acts through another mechanism altogether.
Studies indicate it could even promote bone growth stimulation while helping prevent degenerative conditions like osteoporosis. Or try Level’s THCA Protab, an easy-to-use tablet which dissolves under your tongue over 4-5 hours to become active; or find pure THCa powder to use when cooking or baking – though be careful as any heat exposure could convert this form into THCA!
THCA and THCv Products
As the potential benefits of THCa and THCv become more widely recognized, a growing number of products are being developed to harness these cannabinoids. These products range from flowers and pre-rolls to highly concentrated extracts, offering consumers a variety of ways to incorporate THCA and THCV into their wellness routines.
High THCA Pre-Rol

Herban Bud’s High THCA Pre-Roll offers an accessible way to experience the potential benefits of THCA. This pre-roll is made from high-THCA flowers, allowing users to enjoy the non-psychoactive properties of THCA without the need for specialized equipment. As THCA is heat-sensitive and converts into THC when heated, consuming it in pre-roll form can provide a balanced combination of THCA and THC effects.
Exotics THCA Flower

The Exotics THCA Flower is a product for those who prefer consuming cannabis in its most natural form. Rich in THCa, this flower can be used in any way traditional cannabis flower is used. Whether smoked or vaporized, the Exotics THCa Flower allows users to experience the potential therapeutic properties of this unique cannabinoid.
THCA Diamonds

For those looking for a highly concentrat form of THCa, Herban Bud’s THCa Diamonds may be the perfect fit. THCa diamonds are one of the purest forms of THCa available on the market, often reaching over 95% purity. They are produced through a complex extraction process that isolates and crystallizes THCa, resulting in a product that can be dabb or add to a flower for an enhanced experience.
Usage
THCA is non-psychoactive in its natural state; however, when heated (via smoking or cooking), it undergoes decarboxylation and becomes THC. Although similar effects to THC exist with less intense effects. Therefore it makes an excellent option for medical users or new cannabis consumers looking for something less intense.
THC interacts with CB1 receptors in the brain that produce an intoxicating “high” associated with marijuana use; in contrast, THCa does not interact with them similarly and thus does not cause its intoxicating effects – making THCA undetectable on standard drug tests

Low concentrations of THCV have the ability to promote cell division within the body and therefore aid in treating a variety of ailments including diabetes and metabolic disorders, nausea and vomiting, or reduce them altogether.
Research into THCV is in its infancy, yet it seems to offer promising therapeutic properties. One study revealed that it inhibited production of nitrite by inflammatory macrophages; this may reduce neurodegenerative disorders’ severity. For now, until more research becomes available it’s recommend taking THCV in small doses; you can find it naturally occurring in hemp and cannabis strains, or extracted using chromatography extraction and sold as transdermal patches.
Medical Benefits
Both THCA and THCV have shown potential medical benefits, but they differ in their therapeutic profiles. THCA is not for its anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, anti-emetic, and anticonvulsant properties.
These qualities suggest it may be beneficial for conditions such as arthritis, neurodegenerative disorders, and epilepsy. THCv, on the other hand, has been studied for its potential appetite-suppressing effects, which could be useful for weight management. Additionally, its observed effects on blood sugar levels and insulin resistance suggest a potential role in managing diabetes.
Further, its potential antipsychotic and anti-inflammatory properties may make it useful for managing mental health disorders and inflammatory conditions.
Effects
THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) is a nonpsychotropic comp found in raw cannabis that acts as the precursor to THC. Through decarboxylation (removing of carboxyl groups through heat), THCA can be transform into THCV, producing psychoactive effects.
THCA is less potency than THCV, requiring higher dosage to produce psychoactive effects. Because it doesn’t bind well with CB1 receptors in our endocannabinoid system, THCa doesn’t cause a “high” feeling but instead helps create relaxation, giggles, and happiness while stimulating appetite stimulation. Additionally, THCA acts as a strong appetite stimulant.

Notable effects of THCA include improving mood and lowering blood pressure. THCa can provide relief to patients experiencing discomfort and appetite loss from illness or treatment with chemotherapy, including multiple Sclerosis, Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA), Progressive Muscular Atrophy (PMA), post-traumatic Stress Disorder and other motor neuron diseases such as Multiple Sclerosis. Studies have also demonstrated its efficacy against symptoms like Tremors, Muscle Spasms and Nausea; plus it can boost metabolism which could aid weight loss.
Potential Side Effects of THCa and THCv
While both THCa and THCv are generally considere safe, more research is need to fully understand their potential side effects and long-term risks. As with any cannabinoid, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before using THCa or THCv, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking medications.
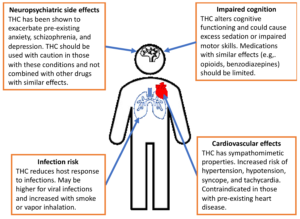
Some possible side effects of THCa and THCv may include dizziness, dry mouth, and changes in appetite. These effects are typically mild and temporary, but it is crucial to monitor your body’s response and adjust usage as needed.
